AdSense RPM optimization is one of the most effective ways to increase website revenue without increasing traffic. For publishers using Google AdSense, RPM determines how much money is earned per 1,000 page views and reflects the true value of website traffic. Understanding how AdSense RPM works and how it can be optimized allows website owners to improve monetization by focusing on user intent, advertiser demand, content quality, and ad placement instead of relying only on page views or clicks.
While most beginners believe that earning more from AdSense depends only on clicks or CPC, experienced publishers understand that RPM represents the combined impact of traffic quality, user behavior, advertiser demand, and ad placement strategy.
Technical Definition
AdSense RPM is calculated by dividing your estimated earnings by the total number of page views and multiplying the result by 1,000.
However, this formula only shows the output, not the mechanism behind RPM growth.
Practical Meaning of AdSense RPM
If your website has:
-
High user engagement
-
Commercial or problem-solving content
-
Visitors from advertiser-rich countries
-
Ads placed where users naturally focus
Then advertisers are willing to pay more to show ads on your pages—even if users click less frequently. This is why two websites with the same traffic can have completely different RPM values.
👉 In simple words:
AdSense RPM is a reflection of how useful your audience is for advertisers, not how many ads you show.
Why AdSense RPM Is the Most Important Metric for Publishers
Most publishers track:
-
Page views
-
CPC
-
CTR
But professionals track RPM first, because RPM answers one critical business question:
“If I increase my traffic by 10,000 page views, how much money will I actually make?”
RPM allows you to:
-
Forecast earnings
-
Identify high-value content
-
Decide which topics to scale
-
Improve monetization without increasing traffic
That is why RPM optimization is the fastest and safest way to increase AdSense revenue—especially when traffic growth is slow.
STEP-BY-STEP PROCESS (VERY DETAILED, PRACTICAL & IMAGINATIVE)
Ab niche main same steps ko rewrite kar raha hoon, lekin is baar:
-
Process clearly dikhega
-
Reader ko lagega “haan, aise hota hai”
-
Beginner bhi follow kar sake
-
Professional tone bhi maintain rahe
Step 1: Understand Where Your RPM Is Actually Coming From
Before increasing RPM, a professional publisher first understands current performance deeply, instead of making random changes.
At this stage, your goal is not optimization, but diagnosis.
What You Do in This Step:
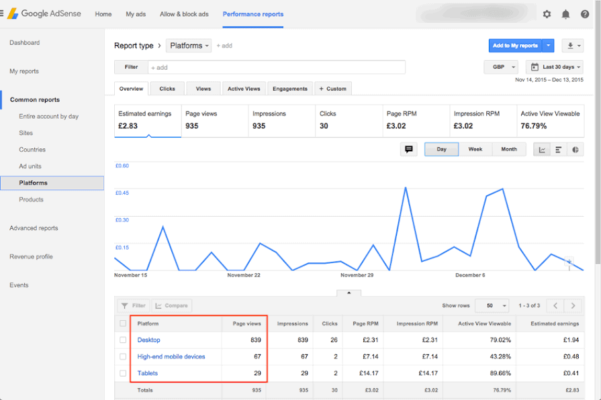
You open your Google AdSense dashboard and go to Reports → Pages. Here, instead of looking at total earnings, you focus on Page RPM.
Now, you will notice something important:
-
Some pages with low traffic generate high RPM
-
Some pages with high traffic generate very low RPM
This immediately tells you that traffic volume is not the problem—monetization efficiency is.
What You Learn:
-
Which topics attract high-paying advertisers
-
Which content formats perform better
-
Which pages deserve more attention
Step 2: Identify Why Certain Pages Have Higher RPM
Now you move one level deeper.
You open a high-RPM page and ask:
-
What is the intent of this page?
-
Is the user trying to solve a problem?
-
Is the content related to tools, money, services, or decisions?
Most high-RPM pages fall into categories like:
-
Comparisons
-
Reviews
-
Solutions
-
Pricing-related topics
This happens because advertisers bid aggressively on decision-making content.
Professional Insight:
Advertisers do not pay for curiosity.
They pay for intent.
So your RPM increases when your content matches buyer or solution intent, even if traffic is lower.
Step 3: Align Content With Advertiser Intent (Not Just SEO Intent)
Many blogs fail because they only optimize for search engines, not advertisers.
In this step, you rewrite or expand content so that:
-
The problem is clearly defined
-
Solutions are discussed in depth
-
Tools, services, or options are naturally mentioned
-
Content feels “decision-ready”
This does not mean promoting anything, but structuring content in a way advertisers want their ads to appear next to.
Step 4: Improve User Engagement to Increase Ad Value
RPM does not increase when users leave quickly.
Advertisers pay more when:
-
Users scroll
-
Users read longer
-
Users interact with content
So at this stage, you optimize:
-
Paragraph length
-
Headings clarity
-
Visual spacing
-
Tables and lists
This keeps users engaged, which increases ad exposure time, leading to higher RPM.
Step 5: Strategic Ad Placement (Not More Ads)
Now comes one of the most misunderstood steps.
Professional publishers do not add more ads.
They move ads where attention already exists.
This includes:
-
After the first meaningful paragraph
-
Between content sections
-
Near comparison tables
-
Sticky placements (without hurting UX)
The goal is visibility without disruption.
Step 6: Improve Traffic Quality Instead of Traffic Quantity
At this stage, you analyze traffic sources.
You might discover:
-
Social traffic has low RPM
-
Tier-1 country traffic has 3–5x higher RPM
-
Mobile vs desktop RPM difference
Now you focus your content, SEO, and promotion on high-value users, not everyone.
This single change alone can double RPM without increasing traffic.
Step 7: Speed, UX & Trust Signals
Fast-loading pages:
-
Increase engagement
-
Reduce bounce rate
-
Improve ad viewability
You optimize:
-
Page speed
-
Layout stability
-
Readability
-
Trust signals (author bio, structure, clarity)
Advertisers prefer clean, trustworthy environments.
Step 8: Continuous Testing & Refinement
RPM optimization is not a one-time task.
Professionals:
-
Test layouts
-
Compare RPM weekly
-
Remove low-performing ads
-
Expand high-performing topics
Small improvements compound over time.
Final Professional Conclusion
AdSense RPM optimization is not about tricks or shortcuts—it is a systematic process that combines content intent, user behavior, advertiser demand, and technical performance.
When done correctly, RPM growth feels natural, predictable, and scalable. That is why professional publishers focus on RPM first, traffic second.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a good AdSense RPM?
A good AdSense RPM depends on your niche, audience location, and content intent. For most blogs, an RPM between $5 and $15 is considered decent, while finance, SaaS, and B2B websites can achieve $20+ RPM. With proper AdSense RPM optimization, even low-traffic websites can significantly increase earnings by improving content quality and traffic value.
Can AdSense RPM be increased without increasing traffic?
Yes, AdSense RPM can be increased without increasing traffic. By focusing on AdSense RPM optimization, publishers can improve ad placement, target high-intent keywords, enhance user engagement, and attract higher-value advertisers. These improvements increase revenue per 1,000 page views without needing more visitors.
How long does it take to see results from AdSense RPM optimization?
Most publishers start noticing RPM improvements within 2 to 4 weeks after implementing optimization changes. However, sustainable AdSense RPM optimization is an ongoing process that involves testing ad placements, refining content, and improving traffic quality over time for long-term growth.
Does ad placement affect AdSense RPM?
Yes, ad placement has a major impact on AdSense RPM. Ads placed within high-visibility areas such as after the first paragraph, inside content sections, and near comparison tables usually perform better. Strategic ad placement improves viewability and engagement, which directly supports AdSense RPM optimization.
Is AdSense RPM optimization safe and compliant with Google policies?
AdSense RPM optimization is completely safe when done correctly. It focuses on improving user experience, content relevance, and ad visibility without forcing clicks or misleading users. As long as publishers follow Google AdSense policies, RPM optimization is a sustainable and policy-compliant monetization strategy.
Read More: How to Increase AdSense CTR Without Increasing Traffic